9th Physics Chapter 1 2025 Short Questions
9th Physics Chapter 1 2025 is about Physical quantities and measurements.
we will check about physical quantities, non-physical quantities, base units and derived units, precision and accuracy and scientific notation also.
We will also check the difference between vernier callipers and micro meter screw gauge, different types or errors and uncertainty in measurement.
One of our tasks is to check the significant figures and rounding off digits.
Q 1.1 Can a non-physical quantity be measured ? If yes, then how ?
Page 06
No. With the help of using tools and instruments, we cannot measure a non-physical quantity because it does not have a defined physical unit. Love, beauty, honesty and trust are non-physical quantities.
==========================================
Q 1.2 What is measurement ? Name its two parts
Page 07
Measurement is a process of comparison of an unknown quantity with a standard quantity (unit).
Page 08
Measurement consists of two parts, a number (magnitude or numerical value) and a unit. In 5 meters, 5 is magnitude and meter is unit.
==========================================
Q 1.3 Why do we need a standard unit for measurement ?
Page 08
Standard unit for measurement can be for efficient working and growth of trade, business and share scientific information.
==========================================
Q 1.4 Write the name of 3 base quantities and 3 derived quantities.
Page 08
Base quantities are length, mass and time.
Page 09
Derived quantities are area, volume and speed.
==========================================
Q 1.5 Which SI unit will you use to express the height of your desk ?
To express the height we will use meter.
==========================================
Q 1.6 Write the name and symbols of all SI base units.
Page 08
| Name of Unit | Symbol of Unit |
|---|---|
| Meter | m |
| Kilogram | kg |
| Second | s |
| Kelvin | K |
| Ampere | A |
| Candela | cd |
| Mole | mol |
==========================================
Q 1.7 Why prefix is used ? Name three sub-multiples and three multiple prefixes with their symbols.
Page 09
We use prefix to make unit simple and easy. Three sub-multiples are deci, centi and milli denoted by d, c and m respectively.
Three multiples are kilo, mega and giga denoted by k, M and G respectively.
==========================================
Q 1.8 What is meant by:
$$(a)\;5\;pm\;\;(b)\;15\;ns\\(c)\;6\;\mu m\;\;(d)\;\;5\;fs$$
Page 10
$$5\;pm\;means\;\;5\;pico\;meters\\15\;ns\;means\;15\;nano\;seconds\\6\;\mu m\;means\;\;6\;micro\;meter\;\;\\5\;fs\;means\;\;5\;femto\;seconds$$
==========================================
Q 1.9 (a) For what purpose, a vernier callipers is used ?
(b) Name its two pain parts.
(c) What is meant by zero error
A vernier callipers measures small lengths with high precision.
There are two main parts of vernier callipers, main scale and vernier scale.
If the zero of the main scale and zero of the vernier scale do not exactly coincide with each other, then there is a zero error in that vernier calliper.
==========================================
Q 1.10 State least count and vernier scale reading as shown in the figure and hence, find the length.
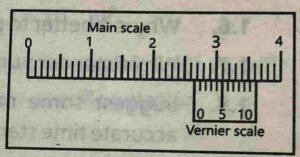
Least count of vernier callipers is 0.01 cm.
$$\style{font-size:12px}{Length\;of\;object\;is\;equal\;to\;\\Main\;scale\;reading+\\(least\;count\times Vernier\;scale\;reading)}$$
Length = 2.6 + (0.01) (4) = 2.6 + 0.04 = 2.64 cm
==========================================
Q 1.11 Which reading out of A, B and C shows the correct length and why ?
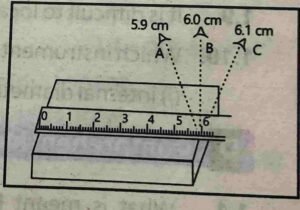
B is correct because the eye is in line with the mark and perpendicular to the scale.
==========================================




