9th math paper 2025 Federal Board Solution
9th math paper 2025 Federal Board Solution. we will completely solve 9th math paper 2025 federal board
Time allowed: 2:40
Total Marks Section B and C: 60
Section B – (Marks 36)

Q2 Attempt the following parts
(i) Simplify the expression
$${\lbrack{(2\;a^\frac12\;b^3)}^4\;x\;\;{(4\;a^{-2}\;b^{-6})}^\frac{-1}2\rbrack}^\frac13\\\\\\$$
$$=\;{\lbrack{(2)}^4\;{(a^\frac12)}^4{(b^3)}^4\times{(4)}^\frac{-1}2{(\;a^{-2})}^\frac{-1}2{(b^{-6})}^\frac{-1}2\rbrack}^\frac13\\\\{=\;\lbrack{(2)}^4\;{(a^{\frac12x4})}{(b)}^{3×4}\times{(2^2)}^\frac{-1}2{(\;a)}^{\frac{-1}2x(-2)}{(b)}^{\frac{-1}2x(-6)}\rbrack}^\frac13\\\\{=\;\lbrack{(2)}^4\;{(a)}^2{(b)}^{12}\times{(2)}^{2x\frac{-1}2}{(\;a)}^1{(b)}^3\rbrack}^\frac13\\\\{=\;\lbrack2^4\;a^2b^{12}\times\;2^{-1}a\;b^3\rbrack}^\frac13\\\\{=\;(2^{4-1}\;a^{2+1}\;b^{12+3}\;)}^\frac13\\\\{=\;(2^3\;a^3\;b^{15}\;)}^\frac13\\\\{=\;(2^3)}^\frac13\;{(a^3)}^\frac13\;{(b^{15})}^\frac13\;\\\\=\;{(2)}^{3x\frac13}\;{(a)}^{3x\frac13}{(b)}^{15x\frac13}\\\\=\;2^1\;a^1\;b^5\\\\=\;2a\;b^5\\\\$$
Question:
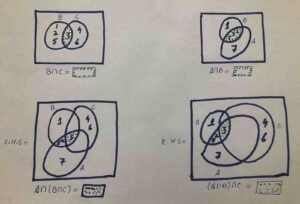
Verify $$A\cap(B\cap C)\;=\;(A\cap B)\cap C\\for\;the\;given\;sets\;u\sin g\\Venn\;diagram\\A=\{2,3,5,7\}\;\;B=\{1,2,3,5\}\;\\and\;\;C=\{3,4,6\}\\\\\\\\\\\\\\$$
Solution:
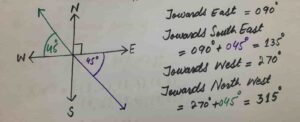
(ii) On what bearing is a ship sailing if it is heading position is ?
(a) towards East (b) towards South East (c) towards West (d) towards North East
Towards East = 090 Towards South East = 090 + 045 = 135
Towards West = 270 Towards North East = 270+045 = 315
Question:
For the given sets: X = { 1,9} Y = { 2,4,6 }
(a) Find Cartesian product xXy
(b) List all the ordered pairs of the relation $$R\;=\;\{\;(x,y)\;:\;x\in X,\;y\in Y,\;x>y\;\}$$
Solution:
(a) xXy = { (1,2),(1,4),(1,6),(9,2),(9,4),(9,6) }
(b) R = { (2,2),(2,4),(9,6) }
$$(iii)\;\;A\;radioactive\;subs\tan ce\\decays\;according\;to\;the\;formula\\M\;=\;200\;\times\;10^{-0.05t},\;where\;m\;is\\mass\;in\;grams\;and\;t\;is\;time\;in\;years.\\(a)\;\;Use\;Logarithms\;to\;express\;’t’\\in\;terms\;of\;’M’\\(b)\;\;Find\;time\;’t’\;when\;mass\;’M’\\reduces\;to\;100\;grams.$$
$$M\;=\;200\;\times\;10^{-0.05t}\\\\LogM\;=\;Log(200\;\times\;10^{-0.05t})\\\\LogM\;=\;Log200\;+\;Log10^{-0.05t}\\\\LogM\;-\;Log200\;=\;-0.05t\;Log10\\\\LogM\;-\;Log(100\times2)\;=\;-0.05t\;(1)\\\\LogM\;-\;Log100\;-\;Log2\;=\;-0.05t\\\\\frac{LogM\;-\;Log100\;-\;Log2}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{LogM\;-\;Log\;10^2\;-\;Log2}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{LogM\;-\;2Log10\;-\;Log2}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{LogM\;-\;2(1)\;-\;0.3010}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{LogM\;-\;2.3010}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{Log100\;-\;2.3010}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{2\;-\;2.3010}{-0.05}=t\\\\\frac{-\;0.3010}{-0.05}=t\\\\6.02\;=\;t\\\\t\;\approx\;6\;years\\$$
Question:
Find square root of $$4\;x^4\;+\;12\;x^3\;+29\;x^2\;+30\;x\;+25\\$$
Solution:

(iv) Solve the equation and represent the solution on a real number line $$\frac{3x-5}4\;=\;\frac{2x+1}3\\$$
$$\frac{3x-5}4\;=\;\frac{2x+1}3\\12(\frac{3x-5}4)\;=12(\;\frac{2x+1}3)\\3(3x-5)\;=\;4(2x+1)\\9x-15=8x+4\\9x-8x=4+15\\x=19\\\\\\$$
$$Verification:-\\\frac{3(19)-5}4\;=\;\frac{2(19)+1}3\\\frac{57-5}4\;=\frac{38+1}3\\\frac{52}4=\frac{39}3\\13=13\\Solution\;set\;=\{\;19\;\}\\\\\\$$
Representation on real line

Question:
$$Factorize\;\\\;(x^2\;-7x\;+4)\;(x^2\;-7x\;+5)\;-\;2$$
Solution:
$$(x^2\;-7x\;+4)\;(x^2\;-7x\;+5)\;-\;2\\\\Let\;\;x^2\;-7x\;=\;y\\\\(y+4)\;(y+5)\;-2\\y^2\;+\;5y\;+4y\;+20-2\\y^2\;+9y\;+18\\y^2\;+6y\;+3y\;+18\\y(y+6)\;+3(y+6)\\(y+6)(y+3)\\\\Put\;y\;=\;x^2\;-7x\\\\(x^2\;-7x\;+6)\;(x^2\;-7x\;+3)\\(x^2\;-6x-x\;+6)\;(x^2\;-7x\;+3)\\(x(x-6)-1(x-6))\;(x^2\;-7x\;+3)\\(x-6)(x-1)(x^2\;-7x\;+3)$$
(v) Prove that $$\frac{Sin\theta}{1-Cos\theta}=\;Cosec\theta\;+\;Cot\theta$$
$$L.H.S\;=\;\frac{Sin\theta}{1-Cos\theta}\\\\=\;\frac{Sin\theta}{1-Cos\theta}\times\;\frac{1+Cos\theta}{1+Cos\theta}\\\\=\;\frac{Sin\theta\;(1+Cos\theta)}{1-\;Cos^2\theta}\\\\=\frac{Sin\theta\;(1+Cos\theta)}{Sin^2\theta}\\\\=\;\frac{Sin\theta\;+\;Sin\theta\;Cos\theta}{Sin^2\theta}\\\\=\frac{Sin\theta\;}{Sin^2\theta}+\;\frac{\;Sin\theta\;Cos\theta}{Sin^2\theta}\\\\=\;\frac1{Sin\theta}\;+\;\frac{Cos\theta}{Sin\theta\;}\\\\=\;Cosec\theta\;+\;Cot\theta\\\\=\;R.H.S$$
Question:
Find equation of straight line passing through the point (3,2) and the point
of intersection of given lines x-y-1=0 , x+y-3=0
Solution:
After adding both the equation, we get
2x-4 = 0 So, x=2
After putting x=2 in first equation we get y=1 hence the point is (2,1)
$$(x_1,y_1)\;=\;(3,2)\;\;and\;\;(x_2,y_2)\;=\;(3,2)\\\\y-y_1\;=\;\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}(x-x_1)\\\\y-2\;=\;\frac{1-2}{2-3}\;(x-3)\\\\y-2\;=\;\frac{-1}{-1}\;(x-3)\\\\y-2\;=\;x-3\\\\-2+3\;=\;x-y\\\\-1\;=\;x-y\\\\x-y\;=\;-1\\is\;the\;required\;equation\;of\;straight\;line\\$$
(vi) A 10 m long ladder is leaning against a vertical wall. The foot of the ladder is 6 m away from the base of wall.
Find the angle that ladder makes with the ground and the height at which ladder touches the wall.

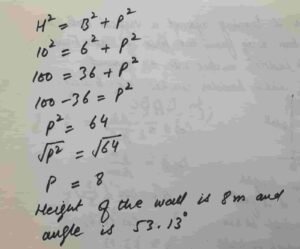
Question:
A bag contains 5 red, 3 blue and 2 green balls. One ball is drawn at random from the bag. Calculate
the probability that (a) The drawn ball is red (b) The drawn ball is not blue
Solution:
$$Sample\;space\;=\;10\;\;Event\;=\;5\\Probability\;of\;red\;=\frac5{10}\;=\;\frac12\;=\;0.5\\\\Sample\;space\;=\;10\;\;Event\;=\;7\\Probability\;of\;red\;=\frac7{10}\;=\;0.7\\$$
(vii) A company wants to install a new cell phone tower so that it is equidistant from two existing towers located at P(2,5) and Q(8,3). Find the equation of locus where the new tower should be placed.
$$Mid\;point\;of\;PQ\;=\;M\\=\;(\frac{2+8}2,\frac{5+3}2\;)\\\;=\;(\frac{10}2,\frac82)\;\;=\;\;(5,4)\\\\Slope\;of\;PQ\;=\;\frac{5-3}{2-8}\;\\=\;\frac{\;2}{-6}\;=\;-\frac13\\\\Slope\;of\;line\;perpendicular\;to\;PQ\;\\=\;\frac1{-\frac13}=3\\\\y-y_1\;=\;m\;(x\;-\;x_1)\\\\y-4\;=\;3\;(x-5)\\\\y-4\;=\;3x-15\\\\y-3x\;=\;-15\;+4\\\\y-3x\;=\;-11\\\\y\;=3x-\;11$$
Question:
Transform the given equation 3x+2y-18 = 0 in
(a) Slope-intercept form y = mx + c
(b) Two-intercept form x/a + y/b = 1
Solution:
(a) $$3x+2y-18=0\\\\3x+2y=18\\\\2y=-3x+18\\\\y\;=\;\frac{-3}2x\;+9\\\\m=\frac{-3}2\;\;and\;\;c\;=\;9$$
(b) $$3x+2y-18=0\\3x+2y=18\\\\\frac{3x+2y}{18}\;=\;\frac{18}{18}\\\\\frac{3x}{18}+\;\frac{2y}{18}\;=\;1\\\\\frac x6\;+\;\frac y9\;=\;1\\\\a=6\;\;and\;b=9$$
(viii) Two similar triangles have area in ratio 25:49. The base and height of smaller triangle are 10 cm and 15 cm, respectively. Find the corresponding base and height of the larger triangle
$$Ratio\;of\;areas\;=\;25:49\;\\=\;\frac{25}{49}\\\\Ratio\;of\;areas\;of\;two\;similar\\triangles\;is\;equal\;to\\the\;square\;of\;the\;ratio\;of\\their\;corresponding\;sides.\\\\Ratio\;of\;corresponding\;sides\\=\sqrt{\frac{25}{49}}=\frac57\\Let\;b\;and\;h\;be\;the\;unknown\;base\\and\;unknown\;height\;respectively\\$$
$$So,\\\frac{10}b=\frac57\\\\70\;=\;5b\\\\\frac{70}5=b\\\\b\;=14\\\\Base\;of\;larger\;triangle\;is\;14\;cm\\\\\frac{15}h=\frac57\\\\105\;=\;5h\\\\\frac{105}5=h\\\\h\;=21\\\\Height\;of\;larger\;triangle\;is\;21\;cm\\$$
Question:
The given data shows the distribution of weights (in kg) of 30 bags of rice. Calculate mean weight of rice bags
If C.I is 05 to 09 then frequency is 5, If C.I is 10 to 14 then frequency is 7, If C.I is 15 to 19 then frequency is 10, If C.I is 20 to 24 then frequency is 4, If C.I is 25 to 29 then frequency is 4.
Solution:
Sum of frequency = 5+7+10+4+4 = 30
Mid point of class intervals respectively = 7,12,17,22,27
Product of frequency and mid point respectively = 35,84,170,88,108
Sum of Product of frequency and mid point = 35+84+170+88+108 = 485
Mean = Sum of frequency divided by Sum of Product of frequency and mid point
Hence, Mean = 485/30 = 16.17 kg
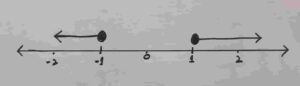
(ix) Solve the inequality, and plot the solution on real number line
$$3x+5\;\leq\;5-3(x+2)\;\leq\;6x-10\;\;\;\forall\;x\in\mathbb{R}\\$$
$$3x+5\;\leq\;5-3(x+2)\;\leq\;6x-10\\\;\\3x+5\;\leq\;5-3x-6\;\leq\;6x-10\\\;\\3x+5\;\leq\;-3x-1\;\leq\;6x-10\\\;\\adding\;1\\\\3x+5+1\;\leq\;-3x-1+1\;\leq\;6x-10+1\\\\3x+6\;\leq\;-3x\;\leq\;6x-9\;\;\\\\Now\;lets\;break\;it\;into\;two\;parts\\$$
$$3x+6\;\leq\;-3x\\\\3x+3x\;\leq\;-6\\\\6x\;\leq-6\\\\\frac{6x\;}6\;\leq\frac{-6}6\\\\x\;\leq\;-1\\\\\\$$
$$-3x\;\leq\;6x\;-\;9\\\\9\;\leq6x\;+3x\\\\9\leq9x\\\\\frac99\leq\frac{9x}9\\\\1\;\leq x\\\\x\geq1$$
$$Solution\;set\;=\;\{\;1\;\leq\;x\;\leq-1\;\}$$
Question:
A fair six-sided die is rolled 60 times. Calculate the expected frequency of
(a) Rolling an even number side (b) Rolling a prime number side
$$Even\;numbers\;=\;\{2,4,6\}\\\\Probability\;of\;Even\;number\;=\;\frac36=\frac12\\\\\\Expected\;frequency\;=\frac12\;\times\;60\;=\;30\\\\Prime\;numbers\;=\;\{\;2,3,5\}\\\\Probability\;of\;Prime\;number\;=\;\frac36=\frac12\\\\\\Expected\;frequency\;=\frac12\;\times\;60\;=\;30$$
Section C – (Marks 24)
Note: Attempt the following parts
Q3 Find HCF and LCM in simplified form using factorization method.
$$x^6\;-\;1\;,\;x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1$$
$$x^6\;-1\;=\;{(x^2)}^3\;-\;{(1)}^3\;\\=(x^2-1)\;(\;{(x^2)}^2\;+(x^2)\;(1)\;+\;{(1)}^2\;)\\=(x^2-1)\;(x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1)\\=(x+1)\;(x-1)\;(x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1)$$
$$Common\;factor\;=(x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1)\\Uncommom\;factor\;=\;(x^2\;-1)\\HCF\;=\;(x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1)\\LCF\;=\;Common\;factors\;\times\;Uncommon\;factors\\LCM\;=\;(x^4\;+\;x^2\;+1)\;\times\;\;(x^2\;-1)\\=\;x^6\;-\;1$$
Q: Points A(0,0), B(2,0) and C( 1, square root 3) are the vertices of triangle ABC. Find slopes of sides AB, BC and AC also find interior angles A , B and C
Solution:
$$A(0,0),\;B(2,0)\;and\;C(1,\sqrt3)\\\\Slope\;of\;AB\;=\;m_1\;=\frac{y_2\;-\;y_1}{x_2\;-\;x_1}\\\\\frac{0-0}{2-0}\;=\;\frac02\;=\;0\\\\Slope\;of\;BC\;=\;m_2\;=\frac{y_2\;-\;y_1}{x_2\;-\;x_1}\\\\\frac{\sqrt3-0}{1-2}\;=\;\frac{\sqrt3}{-1}\;=\;-\sqrt3\\\\Slope\;of\;AC\;=\;m_3\;=\frac{y_2\;-\;y_1}{x_2\;-\;x_1}\\\\\frac{\sqrt3-0}{1-0}\;=\;\frac{\sqrt3}1\;=\;\sqrt3\\$$
$$Angle\;A\;(\;between\;AB\;and\;AC\;)\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{m_1\;-\;m_3}{1+\;m_1\;m_3}\right|\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{0\;-\;\sqrt3}{1+\;(0)\;(\sqrt3)}\right|\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{-\sqrt3}1\right|\\Tan\theta\;=\;\sqrt3\\So\\\theta\;=\;60^\circ\\$$
$$Angle\;B\;(\;between\;AB\;and\;BC\;)\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{m_1\;-\;m_2}{1+\;m_1\;m_2}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{0\;-(-\;\sqrt3)}{1+\;(0)\;(-\sqrt3)}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{\sqrt3}1\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\sqrt3\\\\So\\\\\theta\;=\;60^\circ\\$$
$$Angle\;C\;(\;between\;AC\;and\;BC\;)\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{m_3\;-\;m_2}{1+\;m_3\;m_2}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{\sqrt3\;-(-\;\sqrt3)}{1+\;(\sqrt3)\;(-\sqrt3)}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{2\sqrt3}{1-3}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\frac{2\sqrt3}{-2}\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|-\sqrt3\right|\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\left|\sqrt3\right|\\\\\\Tan\theta\;=\;\sqrt3\\\\So\\\\\theta\;=\;60^\circ\\$$
Its is an equilateral triangle because all the angles are equal.
Q4 U={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}, A={1,2,5,6}, B={3,5,6,9}, C={3,4,6,10} The Venn diagram shows universal set U and sets A, B and C. Find elements of the following sets using Venn diagram.
$$(a)\;\;A^c,\;B^c,\;C^c\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(b)\;A\cup B,\;{(A\cup B)}^c\;\;\\(c)\;B^c\cap C^c\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(d)\;B\cap C,\;{(B\cap C)}^c$$
(a)
$$A^c\;=\;U-A\\A^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}\;-\;\{1,2,5,6\}\\A^c\;=\;\{3,4,7,8,9,10\}\\B^c\;=\;U-B\\B^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}\;-\;\{3,5,6,9\}\\B^c\;=\;\{1,2,4,7,8,10\}\\C^c\;=\;U-C\\C^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}\;-\;\{3,4,6,10\}\\C^c\;=\;\{1,2,5,7,8,9\}\\\\$$
(b)
$$A\cup B\;=\;\{1,2,5,6\}\cup\{3,5,6,9\}\\A\cup B\;=\;\{1,2,3,5,6,9\}\\{(A\cup B)}^c\;=\;U-A\cup B\\{(A\cup B)}^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}\;-\;\;\{1,2,3,5,6,9\}\\{(A\cup B)}^c\;=\;\{4,7,8,10\}\\$$
(c)
$$B^c\;=\;U-B\\B^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}-\{3,5,6,9\}\\B^c\;=\;\{1,2,4,7,8,10\}\\C^c\;=\;U-C\\C^c\;=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}-\{3,4,6,10\}\\C^c\;=\;\{1,2,5,7,8,9\}\\$$
$$B^c\cap C^c\;=\;\{1,2,4,7,8,10\}\;\cap\;\{1,2,5,7,8,9\}\\B^c\cap C^c\;=\;\{1,2,7,8\}$$
(d)
$$B\cap C\;=\;\{3,5,6,9\}\;\cap\;\{3,4,6,10\}\\B\cap C\;=\;\{3,6\}\\{(B\cap C)}^c\;=\;U-\;B\cap C\\{(B\cap C)}^c=\;\{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10\}\;-\;\{3,6\}\\{(B\cap C)}^c\;=\;\{1,2,4,5,7,8,9,10\}$$
Q: For given regular hexagonal roof ABCDEF of sides measure 6 cm, find (a) Angles AGB and AGH (b) Lengths AH and GH (c) The area of triangle AGB (d) Area of hexagonal roof
(a)
$$Central\;angle\;of\;hexagon\;=\;\frac{360^\circ}6\;=\;60^\circ\\Hence\;\angle AGB\;=\;60^\circ\\GH\;is\;the\;angle\;bisector\;of\;\angle AGB\\So\\\angle AGH\;=\frac{\angle AGB}2=\frac{60^\circ}2=30^\circ\\\\$$
(b)
$$H\;is\;the\;mid\;point\;of\;AB.\;So,\\AH\;=\;GH\;=\;\frac{6\;cm}2=3\;cm\\\\$$
(c)
$$AGB\;is\;an\;equilateral\;triangle.\\\\Area\;of\;equilateral\;triangle\;=\frac{\sqrt3}4\;\times\;square\;of\;side\\\\Area\;of\;triangle\;AGB\;=\;\frac{\sqrt3}4\;\times\;{(6\;cm)}^2\\\\Area\;of\;triangle\;AGB\;=\;\frac{\sqrt3}4\;\times\;36\;cm^2\\\\Area\;of\;triangle\;AGB\;=\;9\sqrt3\;cm^2$$
(d)
$$Area\;of\;regular\;hexagonal\;roof\;\\=\;\frac{3\sqrt3}2\;\times\;square\;of\;side\\\\Area\;of\;regular\;hexagonal\;roof\;ABCDEF\;\\=\;\frac{3\sqrt3}2\;\times\;{(6\;cm)}^2\\\\Area\;of\;regular\;hexagonal\;roof\;ABCDEF\;\\=\;\frac{3\sqrt3}2\;\times\;36\;cm^2\\\\Area\;of\;regular\;hexagonal\;roof\;ABCDEF\\\;=54\sqrt3cm^2$$
Q5 Construct a triangle ABC of sides measure m AB = m BC = m AC =5 cm
(a) Construct perpendicular bisectors of the triangle.
(b) Write down the construction steps.
Solution:
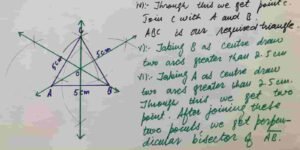
Draw a straight line AB = 5cm
Taking B as centre draw an arc of 5cm and then taking A as radius draw an arc of radius 5 m
Through this we will get point C . Join C with A and B
Taking B as centre draw two arcs greater then half of the length of AB
Taking A as centre draw two arcs of same radius through this we will get two points and then Join these two point.
Its required perpendicular bisector of side AB
In the same manner we will draw perpendicular bisectors of other two sides of triangle ABC
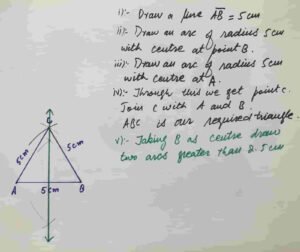
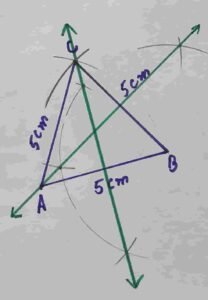
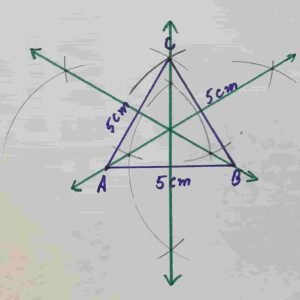
Construction steps of how to draw right bisectors of a triangle

Q Distribution of marks obtained by 50 students in a Mathematics test. Their class intervals are 1-10, 11-20, 21-31 and 41-50 while their frequencies are respectively 5, 10, 15,12 and 8. Calculate the median marks
Solution:
Total frequency = 5+10+15+12+8 = 50
N/2 = 50/2 = 25
Median class is 21-30( Cumulative frequency just reaches or passes 25 )
So, frequency of median = 15
Lower class boundary = mid point of 21 – 0.5 = 20.5
width of class = h = 10
$$Median\;=\;l\;+(\;\frac{{\displaystyle\frac N2}-F}{f_m}\;)\;\times\;h\\\\Median=\;20.5\;+\;\frac{25-15}{15}\;\times\;10\\\\Median\;=\;27.17$$





most of your methods are wrong
then correct them in the comment section
bilkuk sahi
bola
Will the next board paper be easy.
hopefully